![[raised detail]](../images/v/vxt-d1424.jpg)
Padded Emblem/Raised Detail on the Flag of San Cristσbal de la Laguna, Tenerife, Spain (Klaus-Michael Schneider)
![[pale]](../images/v/vxt-d976.gif)
![[pale]](../images/v/vxt-d977.gif)
![[pale]](../images/v/vxt-d2430a.gif)
![[pale]](../images/v/vxt-d2430.gif)
![[pale]](../images/v/vxt-d1724a.gif)
![[pale]](../images/v/vxt-d1724b.gif)
Example; Flag of Hoogstraten, Belgium (fotw);
Arms and Flag of Kaiserslautern, Germany (fotw & Wikipedia);
Arms and Flag of Jerichower Land, Germany (fotw)
2) In some heraldic usage this term relates specifically to the axis of a charge or charges, rather than to its, or their position, on a shield, a banner of arms or a flag but see in pale as referenced above.
![[palewise example]](../images/v/vxt-d2901.gif)
![[palewise example]](../images/v/vxt-d2902.gif)
![[palewise example]](../images/v/vxt-d2903.gif)
Flag of Courtaman, Switzerland (fotw); Flag of
Rudolfstetten-Friedlisberg, Switzerland (fotw); Flag of
Villars-sous-Mont, Switzerland (fotw)
Please note with regard to 2) that charges can be orientated palewise but arranged in fess as per the examples shown below would be blazoned three saw blades palewise in fess
![[palewise example]](../images/v/vxt-d2904.gif)
![[Vaksdal, NO]](../images/v/vxt-d2904a.gif)
Flag and Arms of Siljan, Norway (fotw)
![[flags with pall]](../images/v/vxt-d231.gif)
![[flags with pall]](../images/v/vxt-d231a.gif)
![[flags with pall]](../images/v/vxt-d231b.gif)
![[flags with pall]](../images/v/vxt-d2431.gif)
![[flags with pall]](../images/v/vxt-d2509a.gif)
![[flags with pall]](../images/v/vxt-d2509.gif)
![[flags with pall]](../images/v/vxt-d231c.gif)
From left: National Flag of the Republic of South Africa (fotw); Flag of
Horin, Czech Republic (fotw): Flag of
Krasnoarmeyskiy, Russia (fotw);
Flag of Fontenoy-la-Joϋte, France (Ivan Sache);
Arms and Flag of Matulji, Croatia (fotw);
Flag of the Archbishop of Canterbury, UK (Bartram)
Notes
a) The pall design originated as the pallium, a vestment symbolic of Arch-episcopal authority in some Christian churches
(see also ‘pallia’).
b) With regard to 2) a pile may also be wavy as per the example below.
![[flags with pall]](../images/v/vxt-d2510a.gif)
![[flags with pall]](../images/v/vxt-d2510.gif)
Arms and Flag of Alcobaηa, Portugal (Klaus-Michael Schneider)
Please note, not to be confused with a pall as defined above.
![[pallet]](../images/v/vxt-d1074a.gif)
![[pallet]](../images/v/vxt-d1074b.gif)
![[pallet]](../images/v/vxt-d1725.gif)
Example; Flag of Richterswil, Switzerland (fotw);
Flag of Commugny, Switzerland (fotw)
![[pallia]](../images/v/vxt-d233.gif)
One interpretation of the Pallia given to William
of Normandy in 1066 as shown in the Bayeux Tapestry, and the earliest known representation
of a gonfanon (fotw).
Notes
a) This term was derived from an item of
arch-episcopal regalia – the pallium – and was almost certainly in the majority of cases a
gonfanon.
b)"Pallia" and "pallium" are (respectively) the plural and singular in Vulgate Latin.
![[paly]](../images/v/vxt-d978.gif)
![[Arrissoules, Switzerland]](../images/v/vxt-d979.gif)
![[Wisen, Switzerland]](../images/v/vxt-d2787a.gif)
![[Wisen, Switzerland]](../images/v/vxt-d2787.gif)
![[Wisen, Switzerland]](../images/v/vxt-d1726.gif)
Example: Flag of Arrissoules, Switzerland (fotw);
Arms and Flag of Leipzig, Germany (ICH & fotw);
Flag of Wisen, Switzerland (fotw)

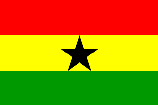



From left: The National Flag of Ethiopia c1897 – 1996; The National Flag of
Ghana (fotw); The National Flag of Senegal (fotw);
National Flag of Benin (fotw); National Flag of
Burkina Faso (fotw)
Notes
a) Some sources include the Garvey and
Rastafarian colours (as referenced above) in this category.
b) Flags that share the same colours, but which do not have the historic or geographic connections given above (for example the flag of Bolivia illustrated below) must not be included in this category.





From left: Arab Revolt/Sharifian Flag 1917 (fotw);
The National Flag of Jordan (fotw);
The National Flag of Syria 1932 - 1958 (fotw);
The National Flag of the United Arab Emirates (fotw);
Flag of Palestine (fotw)
Notes
a) The lines mentioned in the
definition read: “White are our deeds, black the fields of battle, our
pastures are green, but our swords are red with the blood of our enemy.” and
the first flag to used these colours was the Arab Liberation Flag of 1917
(as mentioned and illustrated above).
b) The red, white and black (with or without a touch of green) introduced
by Egypt in their tricolour of 1958 are included by some sources in the above
category but see Arab liberation colours.
c) It should be further noted that flags which share the same colours, but which do not have
the historic or geographic connections given above (for example the flag of
Malawi
illustrated below) must not be included in this category.

National Flag of
Malawi 2010 - 2012 (fotw)





From left: The National Flag of
Russia (fotw); The State Flag of
Serbia (fotw);
The National Flag of the Czech Republic (fotw); National Flag of
Yugoslavia
1992 – 2003 (fotw); National Flag of Croatia (fotw)
a) The red-white-blue tricolour of the Netherlands was almost certainly the model upon which the Russian flag (adopted as a civil ensign c1700) was based, and that some sources include these same “Dutch colours” in the above category – but see ‘Dutch colours 1)’ (also ‘driekleur’ and ‘princeflag’).
b) Flags that share the same colours, but which do not have the historic or geographic connections given above (for example the flag of France illustrated below) must not be included in this category.
![[panel example]](../images/v/vxt-d1149.gif)
![[panel example]](../images/v/vxt-d2016.gif)
![[panel example]](../images/v/vxt-d2017.gif)
![[panel example]](../images/v/vxt-d2018.gif)
Example; Civil Ensign of Malta (fotw); Flag of
Sγo Vicente, Brazil (fotw);Flag of
Guam (fotw)
![[panicles example]](../images/v/vxt-d508.gif)
![[panicles example]](../images/v/vxt-d508a.gif)
![[panicles example]](../images/v/vxt-d508b.gif)
![[panicles example]](../images/v/vxt-d508c.gif)
Flags of a General First Class,
General Second
Class, Lt
General and
Major General, Taiwan (fotw)
![[PMS example]](../images/v/vxt-d2359.gif)
![[PMS example]](../images/v/vxt-d2788.gif)
National Flag of Gabon in Green PMS355, Yellow PMS109 and Blue PMS 293 (fotw);
National Flag of Azerbaijan in Blue PMS 313, Red PMS185 and Green PMS3405 (fotw)

![[pageant standard]](../images/v/vxt-d1494.gif)

![[illustration of a palm]](../images/v/vxt-d234.gif)

